Server configurations
In this step you will add permissions for the account domain user to manage your db and open the Windows firewall rules remotely using SSM
Verify that the EC2 instances are ready before continuing (see progress via the EC2 Console)
Install Failover Cluster role remotely
Use the script provided in LAB 1 (Prerequisites), Step 4 or manually execute the cli commands (on macOS) and run the following command to install the Failover Cluster Role. Be sure to modify the EC2 Instance IDs into your own (see EC2 Console).
Windows
## Install Failover Clustering Role + Management Tools using the script
.\runcommand.ps1 -instanceids i-09a4ee96bexample,i-0b9bfacd2example -commands "Install-WindowsFeature -Name Failover-Clustering -IncludeManagementTools" -region "eu-west-1" -profile workshop -IsLinux $false
macOS
## Send the command to the server
aws ssm send-command --instance-ids "i-0e51d2fc16example" --document-name "AWS-RunPowerShellScript" --comment 'Install failover cluster role' --parameters "commands='Install-WindowsFeature -Name Failover-Clustering -IncludeManagementTools'" --region eu-west-1 --profile workshop
## see the output with **Change the command-id with the output of the previous command
aws ssm get-command-invocation --command-id "d44b1034-3b8e-4db7-9ae2-8fe11138416c" --instance-id "i-0e51d2fc16example" --region eu-west-1 --profile workshop
It will take up to 2-4 minutes,
See example of a good output:
~~~
PS> .\runcommand.ps1 -instanceids i-09a4ee96bbexample,i-0b9bfacd29example -commands "Install-WindowsFeature -Name Failover-Clustering -IncludeManagementTools" -region "eu-west-1" -profile workshop
Creating the document on
i-09a4ee96bbexample
i-0b9bfacd29example
------------------------------------
Working on: i-09a4ee96bbexample
*****Output from the instance:*****
Success Restart Needed Exit Code Feature Result
------- -------------- --------- --------------
True Yes SuccessRest... {Failover Clustering, Remote Server Admini...
WARNING: You must restart this server to finish the installation process.
*****End of output from the instance*****
------------------------------------
Working on: i-0b9bfacd29example
*****Output from the instance:*****
Success Restart Needed Exit Code Feature Result
------- -------------- --------- --------------
True Yes SuccessRest... {Failover Clustering, Remote Server Admini...
WARNING: You must restart this server to finish the installation process.
*****End of output from the instance*****
------------------------------------
Done
~~~
Task 1
Now, change the script parameters / manually use the cli commands to run the following powershell commands:
See solution
~~~
## Install Active directory management tools
.\runcommand.ps1 -instanceids i-09a4ee96bbexample,i-0b9bfacd29example -commands "ADD-WindowsFeature RSAT-AD-Tools" -region "eu-west-1" -profile workshop -IsLinux $false
## Install DNS management tools
.\runcommand.ps1 -instanceids i-09a4ee96bbexample,i-0b9bfacd29example -commands "ADD-WindowsFeature RSAT-DNS-Server" -region "eu-west-1" -profile workshop -IsLinux $false
~~~
macOS Users:
do not use the script, do it manually with the CLI commands aws ssm send-command
See macOS solution
~~~bash
aws ssm send-command --instance-ids "i-0b9bfacd29example" --document-name "AWS-RunPowerShellScript" --comment 'Install AD RSAT' --parameters "commands='ADD-WindowsFeature RSAT-AD-Tools'" --region eu-west-1 --profile workshop
aws ssm send-command --instance-ids "i-0b9bfacd29example" --document-name "AWS-RunPowerShellScript" --comment 'Install DNS RSAT' --parameters "commands='ADD-WindowsFeature RSAT-DNS-Server'" --region eu-west-1 --profile workshop
~~~
Task 2:
Use SSM to open the local Windows Firewall to allow VPC Traffic (10.0.0.0/16)
See solution
windows
.\runcommand.ps1 -instanceids i-0b9bfacd28example,i-0b9bfacd29example -commands "New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName 'Allow local VPC' -Direction Inbound -LocalAddress 10.0.0.0/16 -LocalPort Any -Action Allow" -region "eu-west-1" -profile workshop -IsLinux $false
.\runcommand.ps1 -instanceids i-0b9bfacd28example,i-0b9bfacd29example -commands "New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName 'Allow local VPC' -Direction Outbound -LocalAddress 10.0.0.0/16 -LocalPort Any -Action Allow" -region "eu-west-1" -profile workshop -IsLinux $false
macOS:
do not use the script, do it manually with the following command:
## Send the command to the server
aws ssm send-command --instance-ids "i-0e51d2fc16example" --document-name "AWS-RunPowerShellScript" --comment 'open local firewall' --parameters "commands='New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName \'Allow local VPC\' -Direction Inbound -LocalAddress 10.0.0.0/16 -LocalPort Any -Action Allow'" --region eu-west-1 --profile workshop
aws ssm send-command --instance-ids "i-0e51d2fc16example" --document-name "AWS-RunPowerShellScript" --comment 'open local firewall' --parameters "commands='New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName \'Allow local VPC\' -Direction Outbound -LocalAddress 10.0.0.0/16 -LocalPort Any -Action Allow'" --region eu-west-1 --profile workshop
## see the output with **Change the command-id with the output of the previous command
aws ssm get-command-invocation --command-id "d44b1034-3b8e-4db7-9ae2-8fe11138416c" --instance-id "i-0e51d2fc16example" --region eu-west-1 --profile workshop
Session Manager
Session Manager is a new option for shell-level access.
The Session Manager makes the AWS Systems Manager even more powerful. You can use a new browser-based interactive shell and a command-line interface (CLI) to manage your Windows and Linux instances.
Main features:
-
Secure Access – You don’t have to manually set up user accounts, passwords, or SSH keys on the instances and you don’t have to open up any inbound ports. Session Manager communicates with the instances via the SSM Agent across an encrypted tunnel that originates on the instance, and does not require a bastion host.
-
Access Control – You use IAM policies and users to control access to your instances, and don’t need to distribute SSH keys. You can limit access to a desired time/maintenance window by using IAM’s Date Condition Operators.
-
Auditability – Commands and responses can be logged to Amazon CloudWatch and to an S3 bucket. You can arrange to receive an SNS notification when a new session is started.
-
Interactivity – Commands are executed synchronously in a full interactive bash (Linux) or PowerShell (Windows) environment
-
Programming and Scripting – In addition to the console access you can also initiate sessions from the command line (aws ssm …) or via the Session Manager APIs.
The SSM Agent running on the EC2 instances must be able to connect to Session Manager’s public endpoint. You can also set up a PrivateLink connection to allow instances running in private VPCs (without Internet access or a public IP address) to connect to Session Manager.
Let’s try it (Task 3)
Task 3
Use Session Manager to create a logon script that map the FSx share file (Get the FSx mount url from FSx Console click on “Attach”).
See hint
Logon scripts are saved in “c:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\StartUp"
And the command to map network share is: ‘net use f: \fs-08b8d7a080example.domain.name\share’
See solution
Start session with Session manager and run the following command:
cd "C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\StartUp"
write-output "net use f: \\fs-0a83c90626example.domain.name\share" | out-file FSxMapping.bat -encoding ascii
This script creates a file named “FSxMapping.bat” in “c:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\StartUp" path, with one line: net use f: \fsxmount.name.aws\share.
Output from Session Manager:
PS C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\StartUp> write-output "net use f: \\fs-0a83c90626example.domain.name\share" | out-file FSxMapping.bat -encoding ascii
PS C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\StartUp> ls
Directory: C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\StartUp
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-a---- 6/2/2019 11:57 AM 53 FSxMapping.bat
PS C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\StartUp>
Do the same on the second node
Task 4
Add Sysadmin role to the domain user (Domain\Admin)
See solution
Connect with the RDP client (Windows: built-in tool called mstsc.exe, macOS Microsoft Remote Desktop: ) to the EC2 instances, and authenticate with the local Administrator, (Get the Administrator password from the EC2 console)
Username: .\Administrator
Password: From the EC2 Console
See how to get administrator password with cli command
</span>
</div>
<div class="expand-content" style="display: none;">
<p><strong>Local administrator password</strong>
Get the Local Administrator password through the CLI command
If you are using account from EventEngine - to get the Admin password of the Managed AD, go to the CloudFormation page and select the stack called “module-mysql-workshop-managedADStack-25DM3D50SI6N” (or similar name), go to Parameters tab, and see the Password.
Return to the RDP session, and add the domain\admin to sysadmin role
Open SSMS (SQL Server Management Studio) from the Start Menu, and add the AD domain admin user to sql sysadmin role:
- Security, Right-click on “Logins” and “New Login”
- Click on “Search”
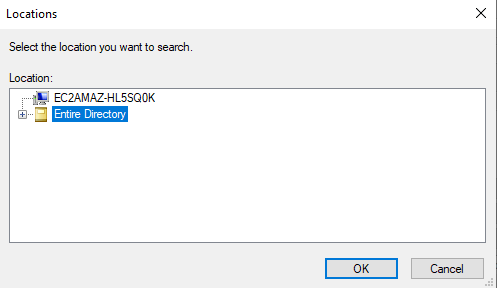
- Click on “Locations”
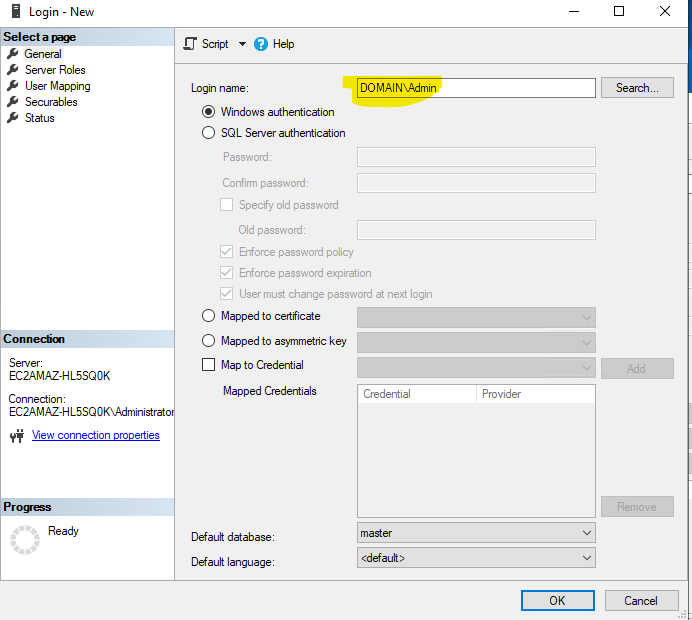
- Authenticate with domain admin : user: “domain\admin” password: (from the CloudFormation template)
- Click “Entire Directory” and OK
-
Now, Search for the user “domain\admin” and click on “Check Names”
-
Click “OK” and you should see :
-
No Go to “Server Roles” and select “Sysadmin”
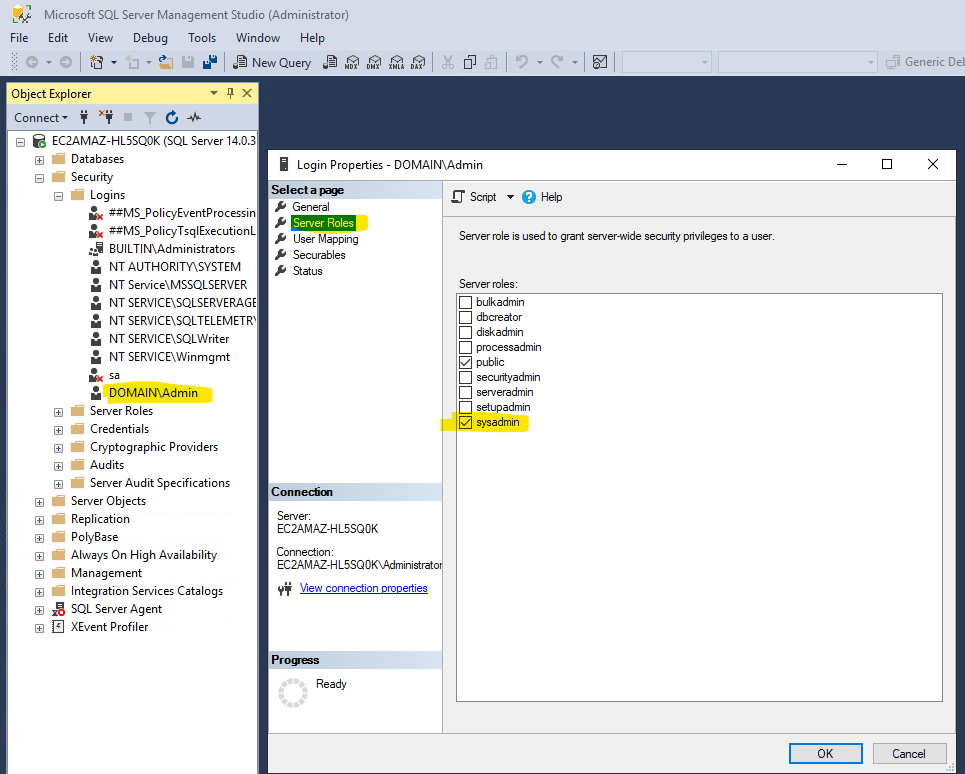
Since the machine is domain joined, you don’t need to use the search, you can simply write Domain\Admin user directly in the user box.
Set the SQL Service to run with the domain user
We want to avoid permissions issues, so we will set the service to use domain user
See solution
Open the SQL Configuration Manager and change the user that runs the SQL Service to domain\admin that you created previously with Managed AD.
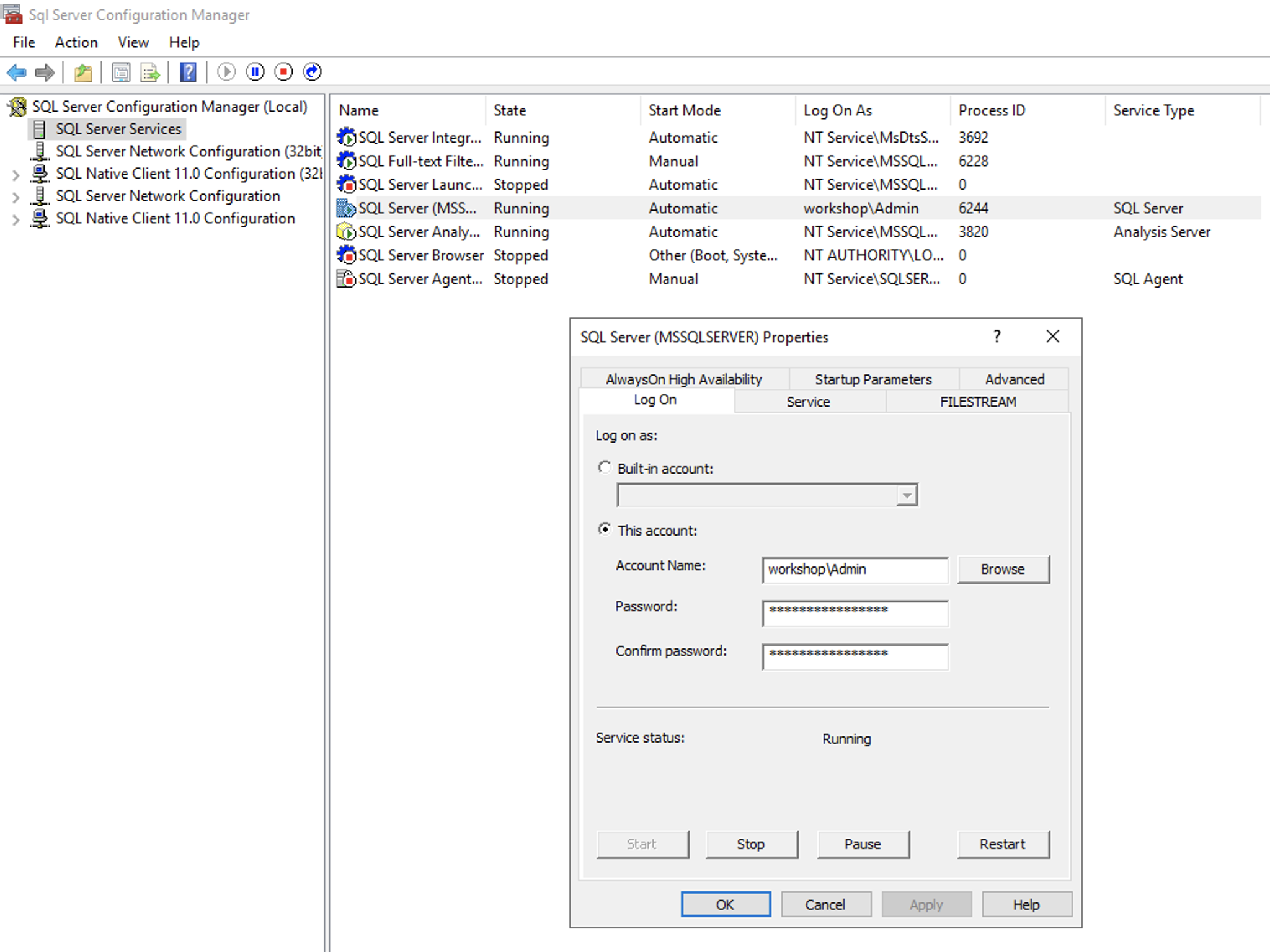
Do the same on the second EC2 instance (add sysadmin role and change the service account)
And restart the servers
Note: In a production environment, it’s best practice to create a SQL service account in AD with minimum permissions.
Connect and Verify
Connect with domain\admin user (After the servers rebooted, you now can connect with RDP and the user domain\admin that you created previously with Managed AD.)
Note: If you are using the account from the workshop, you can see the admin password in the CloudFormation page
Verify your solution:
- Make sure that you have permissions to launch SSMS with the domain user.
- Make sure you see F: drive as the FSx folder
- Open the Windows Explorer and make sure you see all the drives as following: